Newtons three laws in Physics: Newton’s law is the breathe of Classical physics. Newton has three different laws related to motion, mass and energy.
Suppose you slightly kicked a football in front of you. It was seen that it easily moved forward a little.

[ Newtons three laws in Physics ]
Now, also try to push a private car with the same push. It was seen that it did not move forward.

Suppose again, a child is riding on a small bicycle, seeing a truck in the distance, you try to stop the child’s bicycle by pulling it from behind and you can stop.

Would you be able to stop the moving truck if you wanted to by applying the same pull?

In other words, heavier objects show a greater tendency to maintain their stability or mobility. The tendency of an object to maintain its own state is called inertia in physics. The greater the mass of an object, the greater its inertia. Again, the lower the mass of the object, the lower its inertia. Inertia is basically a measure of the mass of an object.
So in order to change the dynamics or stability of an object, it is necessary to apply something, this special thing, when applied, a stationary object moves or wants to move or a moving object becomes stable or wants to become stable, is called force in physics.
In 1687, Sir Isaac Newton provided three formulas in his book, Naturalis Philosophia Principia Mathematica.


T
he formulas shows the relationship between the mass, motion and force of object. These three formulas are called Newton’s formulas or Newton’s laws.
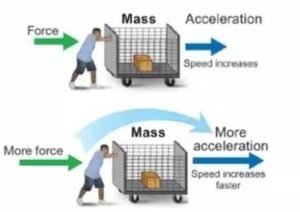
Newton’s first law basically introduces us to the concept of force and inertia. According to this formula, “If no external force is applied, the stationary object will remain stationary forever and the moving object will continue to move in a straight line at the same speed.” That is, just as Force is needed to move an object, so is force needed to bring stability to a moving object. If the force is not applied, the moving velocity of the moving object continues to move in a straight line. It is not possible to find objects in the universe that are not affected by any kind of force.
Then the rate of change of velocity of the object over time will be
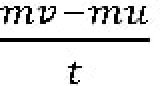
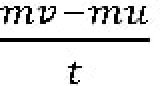
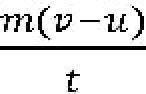
We know that the rate of change of velocity in a given direction is equal to its acceleration. That is a= 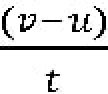
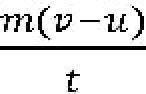
According to the law, ma∝F
Or, ma=kF [k= proportional constant]
Hence the F = ma formula was established which was later widely used in numerous theoretical and applied physics.
In addition, according to Newton’s third law, “Every action has an equal and opposite reaction. According to Newton’s third law, all the forces in the universe are in pairs. If the action force is applied, there must be a response reaction.
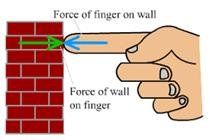
Suppose there is an object A, applied F newton force on another object B. The object B must apply force -F Newton as reaction force. The -ve sign came because of the opposite direction.
Read more:

3 thoughts on “Newtons three laws in Physics”